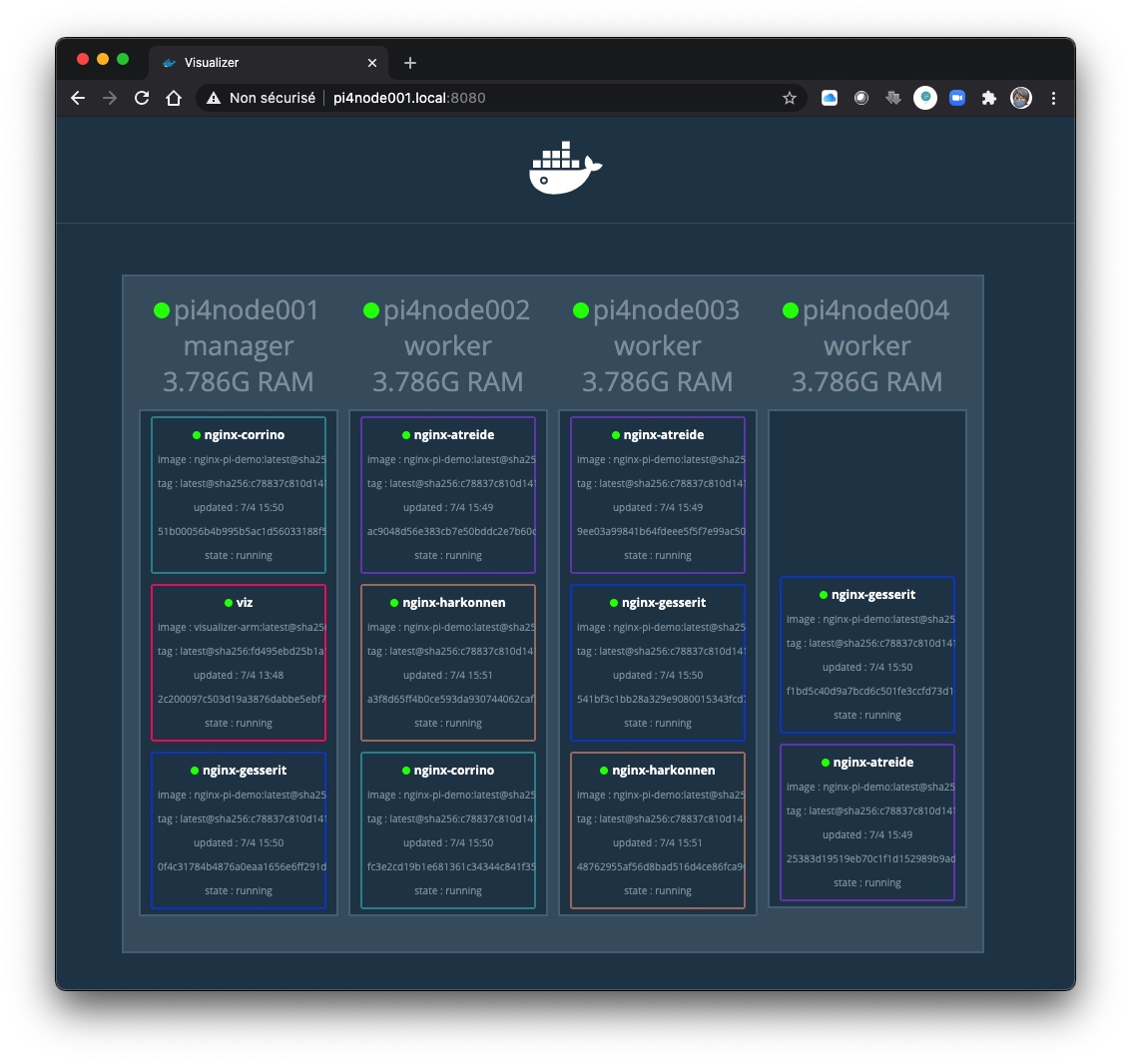
Pour gérer un swarm, il faut, avant tout, obtenir le token…
La syntax est :
pi@pi4node001:~ $ docker swarm join-token "docker swarm join-token" requires exactly 1 argument. See 'docker swarm join-token --help'. Usage: docker swarm join-token [OPTIONS] (worker|manager) Manage join tokens pi@pi4node001:~ $
Donc quand on veut ajouter un node de type MANAGER :
pi@pi4node001:~ $ docker swarm join-token manager To add a manager to this swarm, run the following command: docker swarm join --token SWMTKN-1-2kr5jo0trm2o9bvnypqlzizx1exxivfeitqzi9smnhv6gxsd0f-95rzv0a1mbp0f8k1xkg55176n 192.168.0.201:2377 pi@pi4node001:~ $
et pour un de type WORKER :
pi@pi4node001:~ $ docker swarm join-token worker
To add a worker to this swarm, run the following command:
docker swarm join --token SWMTKN-1-2kr5jo0trm2o9bvnypqlzizx1exxivfeitqzi9smnhv6gxsd0f-8agpq7585s28ppp6gu1ldkf2x 192.168.0.201:2377
pi@pi4node001:~ $
maintenant, il faut se connecter sur le node voulu et exécuter la commande ci-dessus (en fonction du rôle voulu).
Voici un exemple de swarm :
pi@pi4node001:~ $ docker node ls ID HOSTNAME STATUS AVAILABILITY MANAGER STATUS ENGINE VERSION ppyfmhdq6p4xpflqj17eay2cm * pi4node001 Ready Active Leader 20.10.5 pwsktgnu30hvtx5zkgsz4ay2v pi4node002 Ready Active 20.10.5 pi@pi4node001:~ $
Pour ajouter 2 noeuds de type WORKER (notez les hostnames… ):
sur pi4node004:
pi@pi4node004:~ $ docker swarm join --token SWMTKN-1-2kr5jo0trm2o9bvnypqlzizx1exxivfeitqzi9smnhv6gxsd0f-8agpq7585s28ppp6gu1ldkf2x 192.168.0.201:2377 This node joined a swarm as a worker. pi@pi4node004:~ $
sur pi4node003:
pi@pi4node003:~ $ docker swarm join --token SWMTKN-1-2kr5jo0trm2o9bvnypqlzizx1exxivfeitqzi9smnhv6gxsd0f-8agpq7585s28ppp6gu1ldkf2x 192.168.0.201:2377 This node joined a swarm as a worker. pi@pi4node003:~ $
Le résultat est :
pi@pi4node001:~ $ docker node ls ID HOSTNAME STATUS AVAILABILITY MANAGER STATUS ENGINE VERSION ppyfmhdq6p4xpflqj17eay2cm * pi4node001 Ready Active Leader 20.10.5 pwsktgnu30hvtx5zkgsz4ay2v pi4node002 Ready Active 20.10.5 ucelbnf80e6ledibr1qcy9znd pi4node003 Ready Active 20.10.5 awl41iytsw3me002o9gh6u96h pi4node004 Ready Active 20.10.5 pi@pi4node001:~ $